That distinctive aroma of cannabis is delectable for some and pungent for all, but do you know its origin? Cannabis’ signature smell comes from terpene compounds, or terpenoids, that are produced in the flowers and leaves of the cannabis plant. Terpenes are an important component of the cannabis plant, as they work together with cannabinoids and other cannabis compounds to bring you positive benefits.
Learn more as Ivy Hall takes you on a deep dive into the most popular terpenes.
What Are Cannabis Terpenes?
Terpenes are fragrant compounds found in the essential oils of plants, giving them their distinctive flavors and aromas. They also play an essential role in the plant’s growth and survival and have many functions. They appear to use pigmentation and scent to attract pollinators, deter harmful animals, and even exhibit anti-fungal and anti-bacterial properties. Factors such as genetics, indoor/outdoor cultivation, exposure to light, temperature, nutrient levels, and when the plant is harvested will affect the amount of terpenes a cannabis plant will produce.
Terpene can serve as chemical messengers, interacting with other compounds both within the plant and within the human body. After humans consume cannabis, terpenes can work alongside cannabinoids like CBD and THC to influence the human endocannabinoid system (ECS). This system is composed of cannabinoid receptors specially shaped to interact with cannabinoid compounds in the brain, nervous system, and even the gut. The ECS, cannabinoids, and terpenes influence one another to regulate bodily functions like sleep, memory, and similar physiological processes.
What You Should Know About Terpenes
There are as many as 20,000 terpenes, around 150 of which have been identified in the Cannabis Sativa L. plant. However, different strains of cannabis have their own unique collection and concentration of terpenes called a “terpene profile.” With such a large variety of terpenes available in cannabis, it’s important to understand popular terpenes and their effects, how different types work with cannabinoids in the body, and which terpenes may be best for you.
Can I Get High From Terpenes?
While some terpenes are considered to be psychoactive, since they affect the brain, they don’t give you that traditional “high” feeling. That can be attributed to THC, which is a cannabinoid compound and not a terpene. Terpenes are better known for how they influence the overall experience and therapeutic benefits of consuming cannabis.
How Do Terpenes Interact With the Body?
Terpenes are organic compounds. They help regulate our mood, promote well-being, and can have an anti-inflammatory effect. They do so by modulating the way other chemical compounds interact with one another and with the ECS. For example, terpenes can influence the way THC and CBD bind with ECS receptors to reduce anxiety or increase feelings of well-being. Terpenes can also inhibit other chemicals, like cytokines, that cause inflammation, thereby reducing inflammation.
There are three major ways terpenes can exhibit their influence on the body:
Olfactory System
When you smell cannabis, tiny molecules will travel up your nose and into your sinuses. When they arrive, they dissolve in your mucus layer. The cilia (tiny structures that look like hair) in your nose are stimulated, sending an electrical signal through olfactory nerves directly to your brain, where the information is processed.
Respiratory System
When the terpenes are smoked, the molecules travel from your sinuses into the lungs. They reach tiny air sacs known as alveoli and hitch a ride into your bloodstream up to your heart to be pumped around the body. Once they pass the blood-brain barrier, the molecules will interact with neurotransmitters, the brain’s chemical messengers.
Digestive/Circulatory System
Terpenes can also be administered orally, either via edibles or capsules that are swallowed or via tinctures that are held under the tongue (sublingual administration). This sublingual administration allows the terpenes to be passed through the thin skin under the tongue and directly into the bloodstream via hundreds of tiny capillaries. Swallowing terpene means the body will need to digest and metabolize the compounds so they can be passed into the bloodstream. From there, terpenes can reach the brain and ECS receptors.
Exploring the Top Cannabis Terpenes
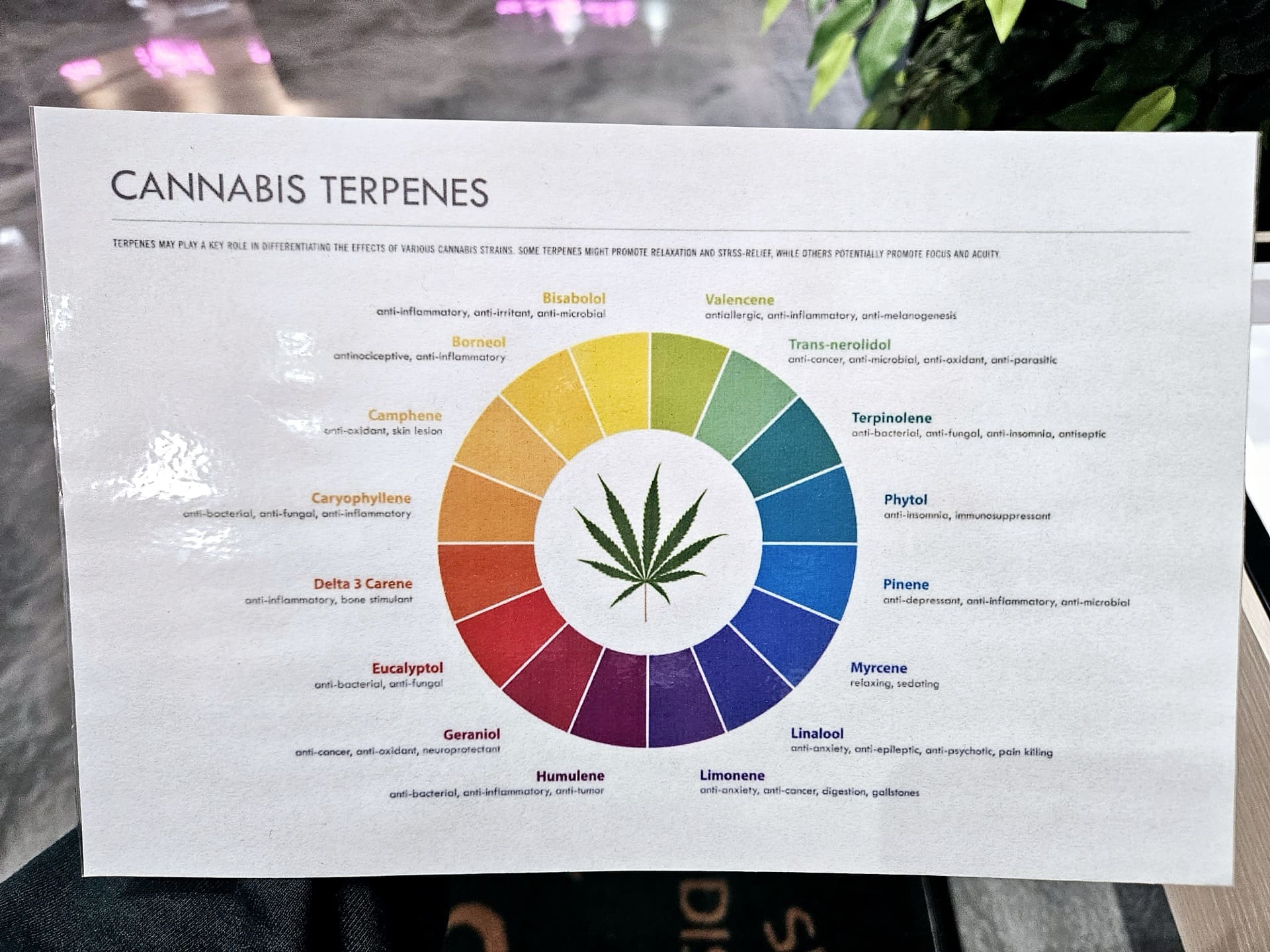
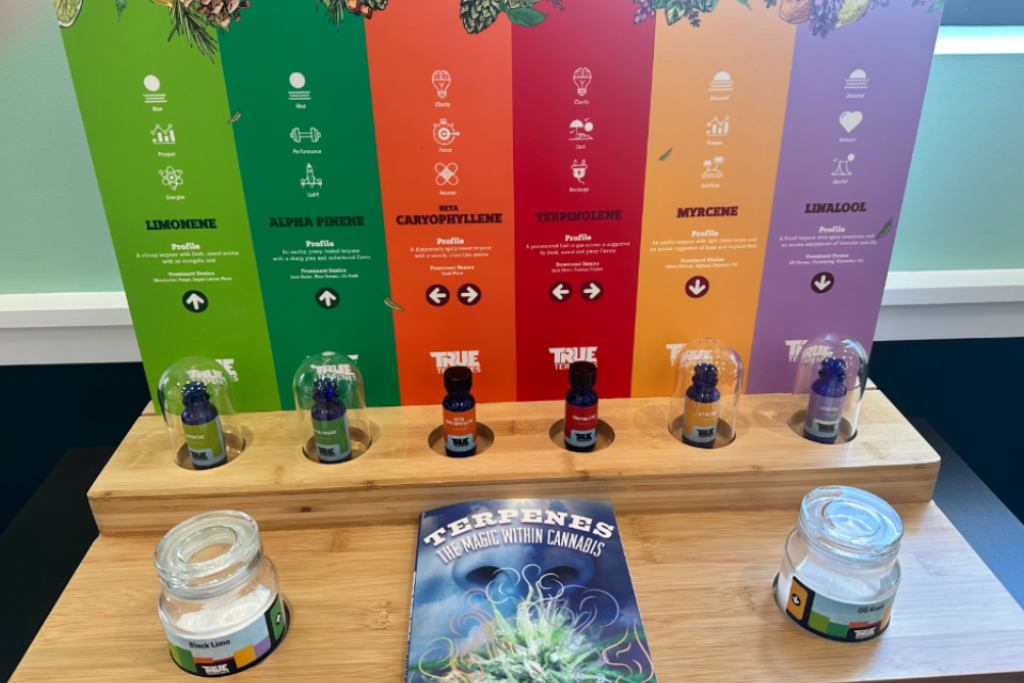
There are hundreds of distinct terpenes that have been identified in cannabis, each possessing unique properties. Different cannabis strains can exhibit specific combinations of these terpenes, contributing to their aromas, flavors, and effects.
The list of terpenes and their effects most commonly found in cannabis, as represented in Ivy Hall’s terpene wheel, are:
Pinene
One of the most researched and popular terpenes found in cannabis is pinene. It is known for its distinctive pine-like aroma, like a walk through a pine forest with earthy and woody undertones. It can also be found in plants such as pine trees, rosemary, and basil.
Pinene helps with mental focus, memory retention, and energy and has been shown to have anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and anti-anxiety properties. It can be beneficial to people who have asthma or are experiencing lung conditions because of its role as a bronchodilator, helping improve airflow to the lungs. Additionally, it is even used as an ingredient in topical antiseptics.
Pinene can be found in popular strains such as Blue Dream and Jack Herer.
Limonene
Limonene is known for its citrusy aroma reminiscent of lemons, oranges, and other citrus fruits. The scent is often described as uplifting and refreshing. Limonene is also found in juniper, peppermint, rosemary, and pine needles.
Research has suggested that limonene has anxiolytic properties, aiding in the production of serotonin and dopamine and reducing anxiety. It may even be beneficial for managing symptoms associated with Attention Deficit Disorder (ADHD), depression, and chronic fatigue. Limonene has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial properties, as well as potential anti-cancer properties. It can relieve gastrointestinal discomforts like acid reflux and heartburn.
Limonene can be found in popular strains like Pineapple Express, Jack Herer, and OG Kush.
Myrcene
Myrcene is known for its earthy, musky aroma with hints of cloves and herbal undertones. It gives some cannabis strains a robust and grounding aroma and is also found in plants like mangoes, hops, thyme, lemongrass, and bay leaves.
Myrcene is known for its sedative and muscle-relaxant properties, promoting deep relaxation and sleep. It additionally has analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial properties.
Black Afghan is a great strain to try if you’re looking for the effects of myrcene.
Linalool
Linalool can be found in over 200 different plants, including lavender, mint, cinnamon, and cilantro. It is best known for its floral aroma, which closely resembles lavender itself.
Linalool is an anxiolytic and an anti-depressant. It appears to have anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antimicrobial benefits. It also has sedative effects, found to promote sleep and alleviate insomnia.
If you’re looking to try a strain that features linalool, try Gone Swishin.’
Caryophyllene
Caryophyllene is known for its spicy, peppery, and woody aroma. This terpene is unique because it directly interacts with the endocannabinoid system. Caryophyllene can also be found in black pepper, cloves, cinnamon, hops, basil, and oregano.
Caryophyllene is anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anxiolytic, and antimicrobial. It is also considered gastroprotective, meaning it can help protect the digestive tract and treat ulcers and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
If you want to try a strain with caryophyllene, we recommend Kush Mints and Sour Diesel.
Terpinolene
Though it is perhaps lesser known than some of the above terpenes, terpinolene is characterized by its complex aroma that blends floral, herbal, piney, and sometimes citrusy notes. It is often described as fresh, woody, and somewhat sweet. It can be found in plants such as apples, lilacs, tea trees, nutmeg, and cumin.
Terpinolene has sedative properties, which provide a calm and soothing effect that aids in sleep. It also has antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory properties and has been found to inhibit the growth of cancer cells and induce apoptosis (programmed cell death).
If you are looking to experience the effects of terpinolene, try the strain known as Florida Oranges.
Humulene
Humulene is known for its earthy, woody aroma with spicy and herbal undertones and is often found alongside myrcene and caryophyllene. Humulene is also found in hops, sage, ginseng, and ginger.
Humulene has anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antibacterial, and antifungal properties. It also may act as an appetite suppressant, potentially helping with weight management. Similar to terpinolene, studies have indicated that humulene may have anti-cancer properties.
Humulene can be found in strains like Moon Boots, Skywalker OG, and Sour Diesel.
Less Common Terpenes
While these terpenes are also found in cannabis, they are not as common and usually come in lower concentrations.
Ocimene
Ocimene has a sweet, citrusy, and herbaceous aroma with floral undertones. It is described as having a fruity and tropical scent. Ocimene is found in mint, parsley, basil, orchids, and kumquats.
Besides its anti-inflammatory, antifungal, antimicrobial, and antioxidant properties, ocimene is known for its potential as a decongestant, relieving nasal congestion and improving airflow.
Eucalyptol
Eucalyptol is known for its refreshing, minty, and slightly spicy aroma. It can be found in eucalyptus trees as well as other aromatic plants such as rosemary, sage, and tea trees.
Eucalyptol has been shown to have anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and analgesic properties. Eucalyptol is also known for its respiratory benefits, which help people with asthma and bronchitis. It has also been suggested that eucalyptol has cognitive-enhancing effects that could help focus, alertness, and mental clarity.
Bisabolol
Bisabolol, also called levomenol, has a subtle floral and sweet aroma with hints of citrus and spice. It is described as having a mild, pleasant scent that is similar to chamomile. It is also found in chamomile flowers and the bark of the Candeia tree.
Bisabolol is a skin-healing anti-irritant that can help calm sensitive skin, reduce redness and inflammation, accelerate healing, and alleviate discomfort. It also has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial properties.
Camphene
Camphene has a pungent, earthy, and herbal aroma with hints of pine. It is also found in conifer trees, such as pine and fir, and herbs like rosemary and sage.
It has been suggested that camphene may have cardiovascular benefits such as lowering cholesterol levels and improving circulation. It also has anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and antifungal properties.
Geraniol
With its sweet, floral aroma and hints of citrus and rose, geraniol is often described as having a delicate and uplifting scent similar to rose bushes. Geraniol is also found in plants like geraniums, lemongrass, and similar aromatic plants.
Geraniol may have neuroprotective effects, such as protecting nerve cells and supporting cognitive function. It is also an anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antimicrobial, and potentially has anti-cancer properties.
Nerolidol
Nerolidol has a floral and woody aroma with hints of citrus and a sweet and slightly earthy scent. Other plants it can be found in are neroli, jasmine, tea tree, and ginger.
Nerolidol is known for its sedative and relaxing effects, which promote sleep and reduce anxiety. Nerolidol is also known to enhance absorption through the skin barrier, and it is antifungal and anti-parasitic.
Valencene
Valencene has a citrusy, sweet, and tangy aroma similar to oranges. It is also found in citrus fruits like grapefruits and tangerines.
While it is not as extensively studied as other terpenes, it does appear to offer anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-cancer properties.
Borneol
Borneol has a minty, camphor-like aroma with hints of pine. It is found in herbs like rosemary, mint, and camphor trees and has been used in traditional medicine for centuries.
It has anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and analgesic properties, and it may have neuroprotective effects, such as supporting cognitive function and protecting nerve cells.
Phytol
Phytol has a mild, floral aroma that is not pungent or dominant. It is found in various green plants. Phytol is typically found in small quantities in cannabis as compared to more abundant terpenes mentioned before, like myrcene or limonene, since it derives from chlorophyll degradation.
Phytol may have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties as well as sedative effects.
The Entourage Effect
In addition to terpenes, cannabis plants contain over 120 different phytocannabinoids, which act on the endocannabinoid system and work to keep your body in balance. CBD and THC are two such phytocannabinoids, though there are many others. Research suggests that taking them together, along with terpenes, is more effective than just taking CBD or THC alone, as they modulate one another’s effects and interactions with the ECS.
This synergistic interaction is called the “Entourage Effect,” and it is often touted for boosting the extended pain relief, stress relief, and inflammation relief capabilities of cannabis.
How To Decide Which Terpenes Are Right for Me

If you are looking to use cannabis terpenes to improve your health and well-being, then you now know that choosing the right strain should be at the top of your priority list. Here are recommendations for finding the right product:
Hunt for Specific Terpenes
Since different terpenes can bring you different benefits, it’s important to identify the terpenes that are best known to provide the benefits you’re looking for. For example, if you’re looking for help with congestion, you should try ocimene. Then, identify cannabis strains that feature that terpene. Using the previous example, consider trying Strawberry Cough or Sour Diesel for congestion.
Don’t Be Afraid to Try Different Types, Combinations, and Dosages
Try experimenting with different combinations of terpenes to find ones that fulfill your needs. Be sure to monitor the effects on your body, and take notes if you need a way to identify those that seem to work better than others. To find the right dose, start slow and note when you begin feeling the effects you’re looking for.
Be Aware of Methods of Consumption
Smoking, vaping, concentrates, tinctures, edibles, capsules, and topicals can all vary your sensory experience. For example, if you inhale the terpenes via smoking or vaping, they are quickly absorbed into your bloodstream, while edibles may take longer to set in but can provide prolonged effects. Tinctures can provide quick effects without the need to inhale smoke or vapor, and topicals can create targeted relief from pain and inflammation.
Find Quality Products
Choosing products from reputable sources will ensure you get top-notch terpene content in your cannabis. Here at Ivy Hall, we are committed to stocking only the best brands in the friendly confines of our boutique dispensary. We take pleasure in not only searching for the broadest variety of terpenes in a carefully curated selection of products but also providing in-shop displays where you can experience the terpene for yourself.
Don’t Be Afraid to Ask a Professional
Ask your local Ivy Hall budtender for advice. While researching on your own will empower you to start your journey, discussing with a pro will help you nail down that perfect cannabis strain for your needs. If you’re not sure which terpenes will best suit you, experience our terpene wheel and interact with our terpene display to get your hands – and your olfactory system – on your top candidates.
Learn before you go with our Terp Time series on YouTube where Ivy Hall budtenders walk you through top cannabis terpenes!
Visit Us at Your Local Ivy Hall Dispensary

At Ivy Hall, we are committed to helping everyone find the right product for their needs. The friendly and knowledgeable staff at our sensory dispensary are here to help whether you are new to cannabis or simply searching for the right combination of terpenes to step up your cannabis game.
Stop by our welcoming neighborhood dispensary to experience these terpenes firsthand, or reach out to us online to learn more.
Resources:
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2024). The Cannabis Terpenes – PMC. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7763918/
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2020). Pharmacology of Indica and Sativa Cannabis. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7120914/
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2022). Terpene Biosynthesis in Cannabis. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8414653/
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2019). Impact of Terpenes on Cannabinoid Receptors. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7324885/
- University of Arizona Health Sciences. (2021). Cannabis Terpenes for Neuropathic Pain Relief. Retrieved from https://healthsciences.arizona.edu/news/releases/study-shows-cannabis-terpenes-may-relieve-chemotherapy-induced-neuropathic-pain
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2021). Terpenes and Their Therapeutic Applications. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10376652/
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2022). Role of Terpenes in Plant Defense Mechanisms. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8703309
- ScienceDirect. (n.d.). Alpha-Pinene: Agricultural and Biological Sciences. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/alpha-pinene
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2021). Linalool and Its Effects. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8348102/
- ScienceDirect. (n.d.). Caryophyllene in Medicine and Dentistry. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/caryophyllene
- ScienceDirect. (n.d.). Terpinolene: Pharmacology and Toxicology. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/pharmacology-toxicology-and-pharmaceutical-science/terpinolene
- ScienceDirect. (n.d.). Humulene in Chemistry. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/chemistry/humulene
- ScienceDirect. (n.d.). Ocimene: Chemistry Insights. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/chemistry/ocimene
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2023). Camphene and Its Pharmaceutical Properties. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9605662/
- PubMed. (2016). The Entourage Effect in Cannabis. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27771935/
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2021). Importance of Terpenes in Cannabis Therapy. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9002489/
- ScienceDirect. (n.d.). Neuroscientific Perspective on Camphene. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/neuroscience/camphene
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2020). Terpenes and Inflammation. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7397177/
- Healthline. (n.d.). Unveiling the Entourage Effect in Cannabis. Retrieved from https://www.healthline.com/health/the-entourage-effect
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2022). Terpenes in Pain Management. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9775512/
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2011). Terpenes and Their Biological Significance. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3165946/
